Return on Expectations (ROE) is a growing trend as it is a practice that is becoming very popular across many organizations. Some of reason behind this growing level of interest among talent development professionals are:
- ROE begins with the end in mind, like many other learning and evaluating practices, ROE is something that needs to be considered in the analysis phase of the design which in bound to get the talent development professionals to consider the results early on.
- Cost effective, compared to other measuring and evolution models such as ROI, the activities that are included in the ROE process are closely related to the common activities that usually take place naturally during the analysis and follow up phases of a learning function. You could also consider ROE as a way to gain the buy-in or pave the way for ROI.
- Early buy-in from stakeholder: ROE involves stakeholders, line managers and the learners very early in the process through gathering their expectation which adds value to the process and increase the buy in
ROE requires the full engagement of business stakeholders for the cycle to close and be successful especially when it is triggered by an external provider.
Capturing and comparing the expectations doesn’t need to be a complex or time consuming process. It is mainly viewed as an opportunity to begin with the end in mind and think about the results based on multiple stakeholders input rather than making assumptions.
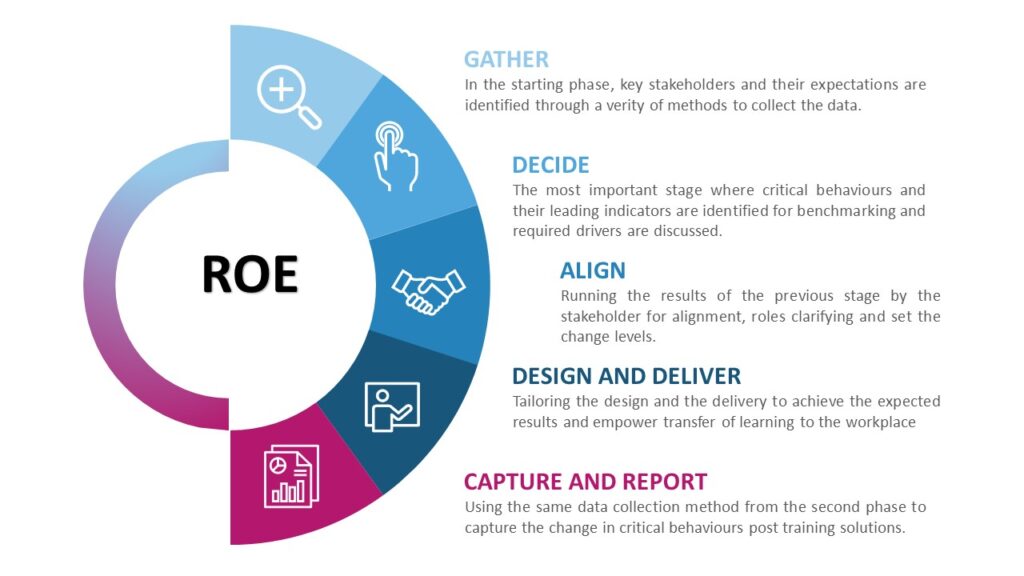
Stages
1. Gather
In the starting phase, key stakeholders and their expectations are identified through a verity of methods to collect the data.
Key activities
- Identify stakeholders
- Communicate with project sponsor
- Create a stakeholders map
- Identify expectations
- Select data collection methods
- Collect data
Examples:
survey sent to the participants to gather expectations from the course
Focus group with a sample of line managers to identify the critical behaviours and link to organization
Interview with key stakeholder : to answer the question “What does success look like?”
Review relevant data : Competency model, Organizational goals, Performance management process
2. Decide
The most important stage where critical behaviours and their leading indicators are identified for benchmarking and required drivers are discussed.
Key activities
- Define Critical behaviours
What are the behaviours that we are looking to change or achieve and how do they link to the organizational benefit. These are usually about making something bigger, better, faster, cheaper, more often, less often, newer.
- Identify key leading indicators
Leading indicators are short-term observations and measurements that suggest that critical behaviours are on track to create a positive impact on desired results.
- Determine required drivers
Required drivers are processes and systems that reinforce, monitor, encourage, and reward performance of critical behaviours on the job. These usually include internal communication and line managers involvement. They are key to the success of the ROE process
- Set Benchmark
Use data collection methods to determine the “current level” of each of the leading indicators as well as the needed recommendations for the drivers.
On a scale from 1-10 :
- How confident do you feel the presenter was
- How often do you feel like the presentations you attend was affected by the presenter lack of confidence
- How confident are you in delivering a presentation assuming you got a minimum of 5 working days to prepare
Output:
a list of expectation per course in the form of critical behaviours and leading indicators
Recommendations for drivers
Manager’s manual for capture stage
3. Align
Running the results of the previous stage by the stakeholder for alignment, roles clarifying and set the change levels.
- Communicate the results of current levels of critical behaviours and leading indicators to key stakeholder
- Align on the required drivers and the roles of learners, line manager and key stakeholders post training to capture the information
- Have a discussion on the expected level after the training journey and would they affect the learning implementation
- Align on the timeline for post training data collection (15,30,60,90 days)
4. Design and Deliver
Tailoring the design and the delivery to achieve the expected results and empower transfer of learning to the workplace
- Deign or adjust the learning experience
- The Trainer then customises the content, to include some tools / case studies that may help address these challenges
- Deliver learning
- Use the same language gathered from learners
- Focus on relevant examples to empower transfer of learning
- Action plan, Designed in a way to make the participants accountable for implementing the learning, and can be shared with their line managers to follow up as part of their PDP’s
- Measure Learning
Kirckpatric levels 1 and 2 during the training event to use as a base for tracking:
- Feedback
- Pre / Post Knowledge Test
- Provide and communicate means:
For the Capture stage introduce the tools during the training and train on it if needed. Example: a survey , action tracker, form
5. Capture and Report
Using the same data collection method from the second phase to capture the change in critical behaviours post training solutions.
- Monitor and adjust
Use the same data collection method from (2.4- Set Benchmark) to capture information post training. 15,30,60 days after the training
Make any adjustments if needed especially in the required drivers
- Report
On comparisons of each of the indicators before and after.
Output: Issue report with the Expectations
In summary, this article discusses the concept of Return on Expectations (ROE) as a growing trend in many organizations. ROE is gaining popularity among talent development professionals for several reasons. It emphasizes starting with the end in mind and involves considering the results early on in the design analysis phase. Compared to other evaluation models like ROI, ROE is cost-effective as it aligns with common activities during the analysis and follow-up phases of a learning function. It also promotes early buy-in from stakeholders, line managers, and learners by gathering their expectations, adding value to the process and increasing engagement.
The ROE process requires full engagement from business stakeholders, especially when triggered by an external provider. The process consists of suggested stages such as gathering expectations, deciding critical behaviors and leading indicators, aligning with stakeholders, designing and delivering tailored learning experiences, and capturing and reporting on the results.
This model and process is something I put together after researching and lot’s of trial and error. I appreciate input and feedback from like minded professionals.

